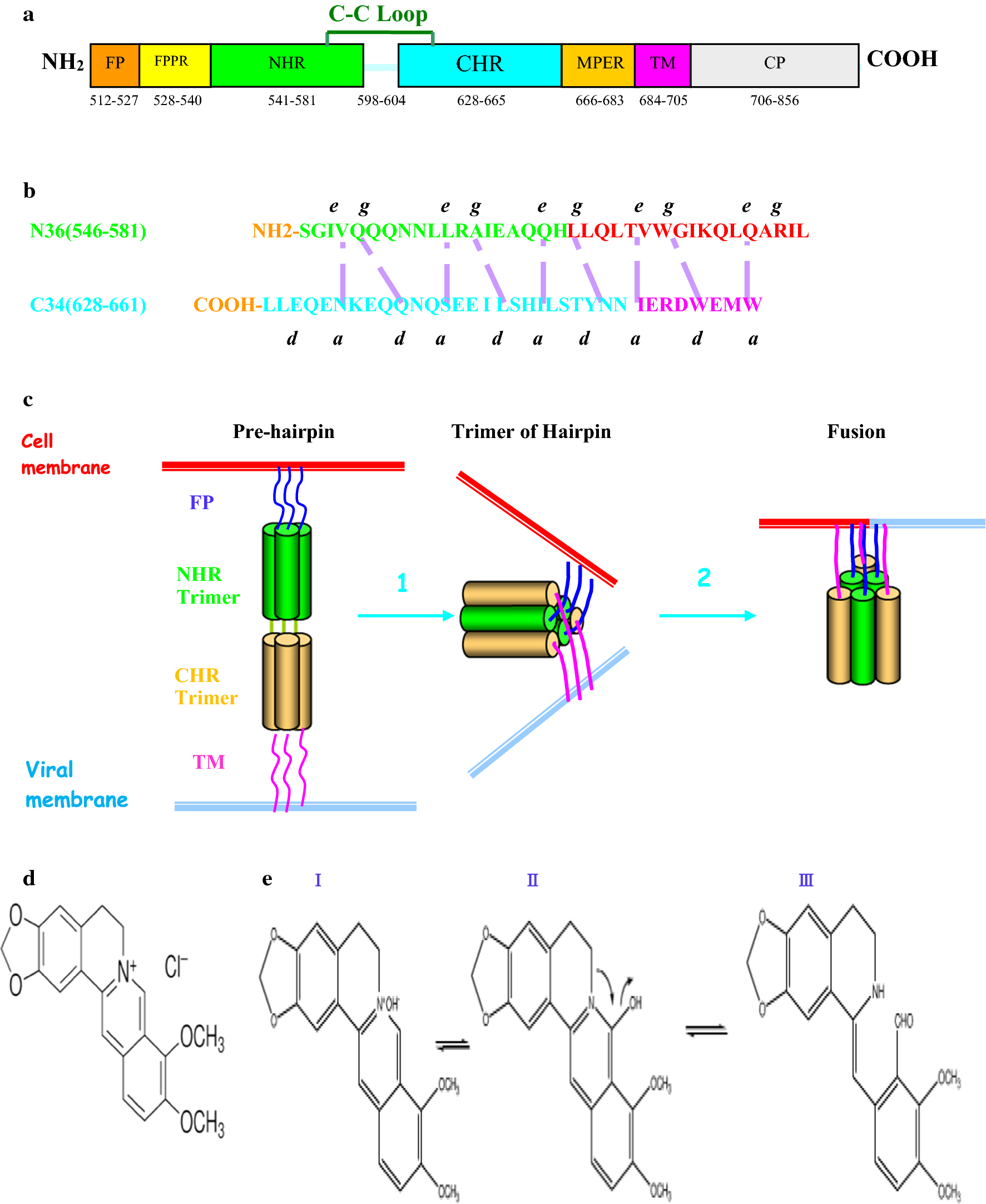
Activity of BBR against viruses of the family Flaviviridae
[...] Hong et al. have shown that
BBR suppresses hepatitis C virus replication by targeting the viral E2 glycoprotein, specifically blocking HCV attachment and entry. Molecular docking studies have indicated that BBR interacts with the HCV E2 glycoprotein [47], suggesting that BBR could be a good candidate for the development of entry inhibitors for the prophylaxis and treatment of HCV infection. The antiviral effect of BBR does not seem to involve modulation of host cell functions such as the interferon response [47–49].
BBR also exhibits antiviral activity against dengue virus (DENV) and Zika virus (ZIKV) infections. Both of these viruses belong to the family Flaviviridae.
Activity of BBR against viral-borne respiratory syndromes
BBR has an inhibitory effect on the NF-κB signaling pathway and therefore might function as an
antiviral agent against coronavirus infection [53, 54]. Recent studies have indicated that an extract from Coptidis rhizoma containing BBR and other protoberberine alkaloids might
inhibit coronavirus RNA synthesis and viral assembly and release [55].
[...] During RSV infection, phosphorylation of p38 MAPK occurs at a very early stage of virus replication, and this phosphorylation can be reduced by BBR treatment. The precise molecular mechanism of this inhibition is still unknown, but recent studies have demonstrated that the effect of BBR is based on its direct interaction with a component of the TLR4 receptor complex. BBR can inhibit TLR4 activation and thus suppress p38 MAPK activation.
In addition, the production of interleukin 6 (IL-6) mRNA upon RSV infection is suppressed by BBR, which indicates its
anti-inflammatory role during RSV infection [58]. It has been shown that BBR functions through several pathways, such as the NF-κB, ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK. As a consequence, these functions
decrease the levels of several proinflammatory cytokines, including tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), interleukin-1 beta (Il-1β), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2). BBR also inhibits the phosphorylation of NF-κB and IκBα) [59].
Anti-influenza activity
Yan et al. showed that
BBR inhibits influenza virus replication in human pulmonary adenocarcinoma cells (cell line A549) and mouse lungs by suppressing the infection. This research confirmed that BBR inhibits the expression of TLR7 and NF-κB, both of which are upregulated in influenza-infected lung tissues [63].
[...] It has been shown that
BBR modulates the generation of proinflammatory substances such as cytokines and stimulates the antiviral state in infected host cells. The potential therapeutic mechanism of BBR in influenza-associated viral pneumonia might be the result of both inhibition of the viral infection and modulation of the release of inflammatory factors [65, 66]. Other studies have shown that BBR and its derivatives also inhibit cytopathogenic effects and neuraminidase (NA) activity in vitro. Enkhtaivan et al. showed that the active site of the viral NA can be blocked by berberine derivatives (BDs) (Table 1) in the same way as it is blocked by the antiviral drug oseltamivir (a well-known NA inhibitor) [65]. The inhibition of viral NA was confirmed in a molecular docking study using BD and the neuraminidases of both influenza A and B viruses [67].
Using this example of the anti-influenza activity of BBR and its derivatives, we can see that BBR is multifunctional and acts through diverse mechanisms. It can attach to protein molecules at their active sites, hence directly blocking their activity, as is the case with the influenza virus NA protein [67], and it can activate different signaling pathways leading to antiviral activity, e.g., inhibition of the expression of TLR7 and NF-κB [64]. The regulatory effects of BBR on the TLR signaling pathway has also been shown to affect the process of intestinal mucosal damage in rats, but the exact molecular interactions between BBR and other molecules remain to be identified. However, based on the existing evidence, we might assume that they rely on binding of BBR to their active sites [68].
Anti-inflammatory properties of BBR
[...] The mechanism of the anti-inflammatory effect of BBR is complex. BBR can inhibit the binding activity NF-κB and activator protein 1 (AP1). AP1 and NF-κB are key transcription factors that are responsible for regulating the expression of many genes involved in inflammation [69]. Moreover, the anti-inflammatory properties of BBR also involve the modulation of MAPKs. BBR can inhibit generation of proinflammatory cytokines and moderate the inflammatory response. During RSV infection, BBR decreases interleukine-6 (IL-6) mRNA level. In influenza virus infection, BBR reduces the mRNA expression of TLR7 and NF-κB in lung tissue [70].
Anti-HPV effect
BBR also suppresses human papillomavirus (HPV) transcription. HPVs are non-enveloped, epitheliotrophic viruses with a circular double-stranded DNA genome that belong to the family Papillomaviridae. Persistent infection with high-risk HPVs, such as HPV16 and HPV18, can lead to the development of cervical cancer. Cancer development and progression are driven by the expression of two oncogenes, E6 and E7. Their expression is mainly dependent on the viral E2 protein and on the availability of the host transcription factor activator protein 1 (AP1). HPV E6 and E7 interact with tumor suppressor proteins, p53 and Rb, respectively. E6 binds and induces ubiquitin-mediated degradation of p53, while E7 inactivates the Rb protein and alters additional cellular signaling pathways that are important for transformation.
BBR can effectively target both the host AP1 and the viral oncoproteins E6 and E7. Inhibition of AP1 and blocking of viral E6 and E7 oncoprotein expression seem to be among the anti-HPV mechanisms of action of BBR [73].
Activity of BBR against members of the families Herpesviridae and Picornaviridae
Low (micromolar) concentrations of BBR can also suppress the replication of different HCMV strains that are resistant to known DNA polymerase inhibitors. HCMV is a member of the family Herpesviridae and has a dsDNA genome. HCMV is responsible for life-threatening pneumonia, gastrointestinal diseases, retinitis, and other conditions after primary infection and in immunocompromised patients. [...] Lunganini et al. showed that BBR interferes with the transactivating function of the HCMV IE2 protein. IE2 plays a critical role in the progression of HCMV replication and in viral pathogenesis and reactivation from latency [74]. It is the most important HCMV regulatory protein and a strong transcriptional activator of viral and cellular gene expression. IE2 binds to DNA and has the ability to interact with cellular transcription factors, which is necessary for regulation of transcriptional activation of viral and host genes and cellular functions [75].
The inhibitory activity of BBR on the IE2-dependent transactivation of early genes depends on activation of MAPKs.
BBR is active against human herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 (HSV 1 and 2) and also against mouse cytomegalovirus (MCMV). HSV infection is characterized by small blisters on the skin or mucous membranes of the mouth, often called “cold sores” or “fever blisters”, and can cause a sore throat. It has been reported that
BBR inhibits DNA synthesis by intercalating into DNA. BBR also inhibits the synthesis of both HSV-1 and HSV-2 late genes and proteins [76]. Inhibitory activity of BBR has also been observed against different genotypes of enterovirus 71 (EV71), which belongs to the family Picornaviridae and has a positive-sense RNA genome.
Anti-HIV activity
BBR and berberrubine along with 9-substituted derivatives of berberine have demonstrated antiviral activity against HIV [80], probably due to inhibition of reverse transcriptase (RT) activity. The use of 20 µg of BBR per reaction resulted in 94% inhibition of HIV-1 RT. An improved therapeutic effect was observed when berberine-9-0 esters were used [80] (Table 1). BBR might therefore have a potential application as a complimentary therapeutic agent against HIV infection.
Plants are a rich source of new antiviral, pharmacologically active agents. The naturally occurring plant alkaloid berberine (BBR) is one of the phytochemicals with a broad range of biological activity, including anticancer, anti-inflammatory and antiviral ...

www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov





 and perhaps only those who are on the low blood pressure side can be just a bit cautious and keep track of that effect.
and perhaps only those who are on the low blood pressure side can be just a bit cautious and keep track of that effect.