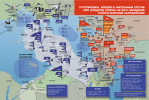
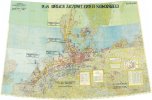
I can still hear my History teacher talking about the German tanks rolling through the Danzig Corridor into Poland.
Yes, after years and years of learning (lies), from the American Civil War, WWI & WWII and wars on either side, unlearning became a greater task, and it's not done by a long shot.
As for WWII (with emphasis on Poland that Thorbiorn brought out), here is the studied Michael Jabara Carley - Prof of history at the Université de Montréal (although it leads off with the Canadian Prime Minister, young Justin, it is looking at Litvinov, a look at Molotov-Ribbentrop, France, Britain, America, Poland (et cetera) and Germany:

The Canadian Prime Minister Needs a History Lesson
On August 23rd the Canadian Prime Minister’s office issued a statement to remember the so-called “black ribbon day,” a bogus holiday established in 2008-2009 by…
snip:
The Soviet Union also tried to improve relations with Poland. Here too Soviet diplomats failed when the Polish government signed a non-aggression pact with Nazi Germany in January 1934. The Polish elite never hid its preference for a rapprochement with Germany rather than for better relations with the USSR. The Poles became spoilers of collective security sabotaging Soviet attempts to organise an anti-German entente. They were at their worst in 1938 as Nazi accomplices in the dismemberment of Czechoslovakia before they became victims of Nazi aggression in 1939. Soviet diplomats repeatedly warned their Polish counterparts that Poland was headed to its doom if it did not change policy. Germany would turn on them and crush them when the time was right. The Poles laughed at such warnings, dismissed them out of hand. Russians are “barbarians”, they said, the Germans, a “civilised” people. The choice between the two was easy to make.
Let me be clear here. The archival evidence leaves no doubts, the Soviet government offered collective security and mutual assistance to France, Britain, Poland, Romania, Czechoslovakia, even fascist Italy, and in every case their offers were rejected, indeed spurned contemptuously in the case of Poland, the great spoiler of collective security in the lead-up to war in 1939. In the United States, the State Department sabotaged improving relations with Moscow. In the autumn of 1936, all Soviet efforts for mutual assistance had failed, and the USSR found itself isolated. No one wanted to ally with Moscow against Nazi Germany; all the above mentioned European powers conducted negotiations with Berlin to lure the wolf away from their doors. Yes, even the Czechoslovaks. The idea, both stated and unstated, was to turn Hitler’s ambitions eastward against the USSR.
Then came the Munich betrayal in September 1938. Britain and France sold out the Czechoslovaks to Germany. “Peace in our time,” Neville Chamberlain, the British prime minister, declared. Czechoslovakia was dismembered to buy “peace” for France and Britain. Poland got a modest share of the booty as part of the dirty deal. “Jackals,” Winston Churchill called the Poles. In February 1939 the Manchester Guardian called Munich, selling out your friends to buy off your enemies. That description is apt.
In 1939 there was one last chance to conclude an Anglo-Franco-Soviet pact of mutual assistance against Nazi Germany. I call it the “alliance that never was”. In April 1939 the Soviet government offered France and Britain a political and military alliance against Nazi Germany. The terms of the alliance proposal were submitted on paper to Paris and London. In the spring of 1939 war looked inevitable. Rump Czechoslovakia had disappeared in March, gobbled up by the Wehrmacht without a shot fired. Later that month Hitler claimed the German populated Lithuanian city of Memel. In April a Gallup poll in Britain showed massive popular support for a Soviet alliance. In France too public opinion backed an alliance with Moscow. Churchill, then a Conservative backbencher, declared in the House of Commons that without the USSR there could be no successful resistance against Nazi aggression.
Logically, you would think that the French and British governments would have seized Soviet offers with both hands. It did not happen. The Foreign Office rejected the Soviet alliance proposal with the French grudgingly trailing behind. Litvinov was sacked as commissar and replaced by Viacheslav M. Molotov, Stalin’s right arm. For a time Soviet policy continued unchanged. In May Molotov sent a message to Warsaw that the Soviet government would support Poland against German aggression if so desired. Incredible as it may seem, on the very next day, the Poles declined Molotov’s proffered hand.