Anthony gives a broad overview of the linguistic and archaeological evidence for the early origins and spread of the Indo-European languages, describing a revised version of
Marija Gimbutas's
Kurgan hypothesis. Anthony describes the development of local cultures at the northern Black Sea coast, from hunter-gatherers to herders, under the influence of the Balkan cultures, which introduced cattle, horses and bronze technology.
When the climate changed between 3500 and 3000 BCE, with the steppes becoming drier and cooler, those inventions led to a new way of life in which mobile herders moved into the steppes, developing a new kind of social organisation with patron-client and host-guest relationships. That new social organisation, with its related Indo-European languages, spread throughout Europe, Central Asia and South Asia because of its possibilities to include new members within its social structures.
Part One covers theoretical considerations on language and archaeology. It gives an introductory overview of Indo-European linguistics (ch. 1); investigates the reconstruction of Proto-Indo-European (ch. 2); the dating of Proto-Indo-European (ch. 3); the specific vocabulary for wool and wheels (ch. 4); the location of the Proto-Indo-European homeland (ch. 5); and the correlation of these linguistic discoveries with archaeological evidence and the role of elite recruitment in language shift (ch. 6).
Part Two covers the development of the Steppe cultures and the subsequent migrations out of the Pontic-Caspian region into Europe, Central Asia, and South Asia. The splitting of the major branches of Indo-European (except perhaps Greek) can be correlated with archaeological cultures, showing steppe influences in a way that makes sense chronologically and geographically in light of linguistic reconstructions. Anthony gives an introduction to Part Two (ch. 7); describes the interaction between Balkan farmers and herders and steppe foragers at the Dniestr River (in western Ukraine) and the introduction of cattle (ch. 8); the spread of cattle-herding during the Copper Age and the accompanying social division between high and low status (ch. 9); the domestication of the horse (ch. 10); the end of the Balkan cultures and the early migrations of Steppe people into the Danube Valley (ch. 11); the development of the steppe cultures during the Eneolithic, including the interaction with the Mesopotamian world after the collapse of the Balkan cultures and the role of Proto-Indo-European as a regional language (ch. 12); the Yamna culture as the culmination of these developments at the Pontic-Caspian steppes (ch. 13); the migration of Yamna people into the Danube Valley and the origins of the western Indo-European languages at the Danube Valley (Celtic, Italic), the Dniestr (Germanic) and the Dnieper (Baltic, Slavic) (ch. 14); migrations eastward which gave rise to the Sintashta culture and Proto-Indo-Iranian (ch. 15); migrations of the Indo-Aryans southward through the Bactria-Margiana Archaeological complex into Anatolia and India (ch. 16); and concluding thoughts (ch. 17).
Part One: Language and Archaeology
Chapter One: The promise and Politics of the Mother Language
Anthony introduces the similarities between a broad range of languages and their common ancestor, Proto-Indo-European. He proposes that "the Proto-Indo-European homeland was located in the steppes north of the Black and Caspian Seas in what is today southern Ukraine and Russia."
[1] Anthony gives a short overview of the history of the linguistical study of PIE
[2] and then presents six major problems that hinder a "broadly acceptable union between archaeological and linguistic evidence."
[3]
Chapter Three: Language and Time 1. The Last Speakers of Proto-Indo-European
Using a mathematical analysis borrowed from evolutionary biology, Don Ringe and Tandy Warnow propose the following evolutionary tree of Indo-European branches:
[4]
- Pre-Anatolian (before 3500 BCE)
- Pre-Tocharian
- Pre-Italic and Pre-Celtic (before 2500 BCE)
- [Pre-Germanic][note 1]
- Pre-Armenian and Pre-Greek (after 2500 BCE)
- [Pre-Germanic];[note 1] Proto-Germanic c. 500 BCE[6]
- Pre-Balto-Slavic;[4]
- Proto-Indo-Iranian (2000 BCE)
Chapter Four: Language and Time 2: Wool, Wheels and Proto-Indo-European
Anthony proposes that the Proto-Indo-European emerged after ca. 3500 BCE. He bases that especially on his analysis of Indo-European terms for wool textiles and wheeled vehicles:
Neither woven wool textiles nor wheeled vehicles existed before about 4000 BCE. It is possible that neither existed before about 3500 BCE. Yet Proto-Indo-European speakers spoke regularly about wheeled vehicles and some sort of wool textile. This vocabulary suggests that Proto-Indo-European was spoken after 4000–3500 BCE.
[7]
Anthony, following the methodology of Ringe and Warnow, proposes the following sequence:
[8]
- Pre-Anatolian (4200 BCE)
- Pre-Tocharian (3700 BCE)
- Pre-Germanic (3300 BCE)
- Pre-Italic and Pre-Celtic (3000 BCE)
- Pre-Armenian (2800 BCE)
- Pre-Balto-Slavic (2800 BCE)
- Pre-Greek (2500 BCE)
- Proto-Indo-Iranian (2200 BCE), split between Iranian and Old Indic 1800 BCE
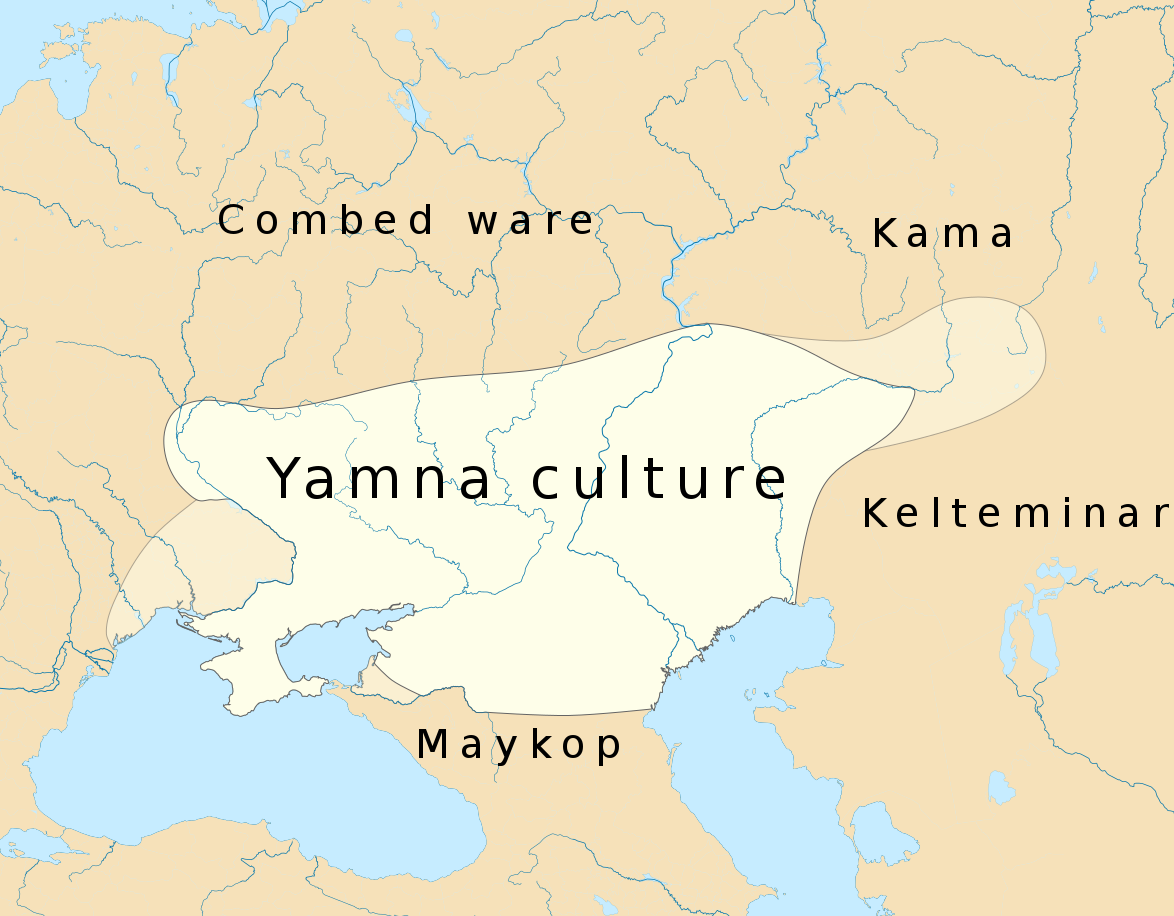
A key insight is that early expansions of the area in which Indo-European was spoken were often caused by "recruitment," rather than only by military invasions. With the
Yamna culture as a nucleus candidate, the original recruitment would be to a way of life in which intensive use of horses allowed herd animals to be pastured in areas of the Ukrainian / South Russian steppe, outside of river valleys.
Part Two: The Opening of the Eurasian Steppes
Chapter Eight: First Farmers and Herders: The Pontic-Caspian Neolithic
Ukraine rivers
According to Anthony, the development of the Proto-Indo-European cultures started with the introduction of cattle at the Pontic-Caspian steppes,
[9], which, until ca. 5200-5000 BCE, were populated by hunter-gatherers.
[10] The first cattle herders arrived from the Danube Valley at ca. 5800-5700 BCE, descendants from the first European farmers.
[11] They formed the
Criş culture (5800-5300 BCE), creating a cultural frontier at the Prut-Dniestr watershed.
[12]
The adjacent
Bug-Dniester culture (6300–5500 BCE) was a local forager culture from which cattle breeding spread to the steppe peoples.
[13] The
Dniepr Rapids area was the next part of the Pontic-Caspian steppes to shift to cattle-herding. It was the most densely-populated area of the Pontic-Caspian steppes at the time and had been inhabited by various hunter-gatherer populations since the end of the Ice Age. From ca. 5800-5200, it was inhabited by the first phase of the
Dnieper-Donets culture, a hunter-gatherer culture contemporaneous with the Bug-Dniestr culture.
[14]
Chapter Nine: Cows, Copper and Chiefs
At ca. 5200-5000 BCE, the non-Indo-European
Cucuteni-Tripolye culture (5200-3500 BCE) appears east of the Carpathian mountains,
[15] moving the cultural frontier to the Southern Bug valley,
[16] and the foragers at the Dniepr Rapids shifted to cattle herding, marking the shift to Dniepr-Donets II (5200/5000-4400-4200 BCE).
[17] The Dniepr-Donets culture kept cattle not only for ritual sacrifices but also for their daily diet.
[18] The
Khvalynsk culture (4700-3800 BCE),
[18] located at the middle
Volga, which was connected with the Danube Valley by trade networks,
[19] also had cattle and sheep, but they were "more important in ritual sacrifices than in the diet."
[20] According to Anthony, "the set of cults that spread with the first domesticated animals was at the root of the Proto-Indo-European conception of the universe"
[20] in which cattle had an essential role.
[21] The
Samara culture (early 5th millennium BCE),
[note 2]
Chapter Ten: The Domestication of the Horse and the Origins of Riding: The Tale of the Teeth
The domestication of the horse had a wide-ranging effect on the steppe cultures, and Anthony has done fieldwork on it.
[26] Bit wear is a sign of horse-riding, and the dating of
horse teeth with signs of bit wear gives clues for the dating of the appearance of horse l-riding.
[27] The presence of domesticated horses in the steppe cultures was an important clue for Marija Gimbutas's development of her Kurgan hypothesis.
[28] According to Anthony, horseback riding may have appeared as early as 4200 BCE,
[29] and horse artifacts show up in greater amounts after 3500 BCE.
[29] Horseback riding greatly increased the mobility of herders, allowing for greater herds, but also led to increased warfare by the need for additional grazing land.
[30]
Chapter Eleven: The End of Old Europe and the Rise of the Steppe
The
Sredny Stog culture (4400-3300 BCE)
[31] appears at the same location as the Dniepr-Donets culture but shows influences from people who came from the Volga River region.
[32] The Sredni Stog culture was "the archaeological foundation for the Indo-European steppe pastoralists of Marija Gimbutas,"
[33] and the period "was the critical era when innovative Proto-Indo-European dialects began to spread across the steppes."
[33]
Around 4200-4100 BCE, a climate change occurred, causing colder winters.
[34] Between 4200-3900 BCE, many tell settlements in the lower Danube Valley were burned and abandoned,
[34] and the Cucuteni-Tripolye culture showed an increase in fortifications
[35] and moved eastwards, towards the Dniepr.
[36]
Steppe herders, archaic Proto-Indo-European-speakers, spread into the lower Danube valley in about 4200-4000 BCE, causing or taking advantage of the collapse of
Old Europe.
[37] According to Anthony, their languages "probably included archaic Proto-Indo-European dialects of the kind partly preserved later in Anatolian."
[38] According to Anthony their descendants later moved into Anatolia at an unknown time, maybe as early as 3000 BCE.
[39] According to Anthony, the herders, forming the Suvorovo-Novodanilovka complex,
[note 3] probably were a chiefly elite from the Sredni Stog culture at the Dniepr Valley.
[41]
Chapter Twelve: Seeds of Change on the Steppe Borders. Maikop Chiefs and Tripolye Towns
The collapse of Old Europe lead to a decrease in copper grave gifts in the North Pontic steppes. Between 3800 and 3300, substantial contact took place between the steppe cultures and Mesopotamia via the
Maikop culture (3700-3000 BCE), in the northern Caucasus.
[42] To the west, Tripolye pottery begins to resemble Sredni Stog pottery, showing a process of assimilation between the Tripolye culture and the steppe cultures and a gradual breakdown of the cultural border between the two.
[43]
Between 3800 and 3300 BCE, five eneolithic steppe cultures can be discerned, and Proto-Indo-European dialects may have then served as a regional language.
[44]
- Mikhaylovka culture (3600—3000 BCE), on the Black Sea coast between the Dniestr and the Dniepr.[45] Mikhailovka I people looked less like the Suvorovo-Novodanilovka people and may have intermarried more with Tripolye culture people or people from the Danube valley.[46] Mikhailovka II upper level (3300-3000 BCE) imported pottery from the Repin culture (see below) and is regarded as early western Yamna.[47] In the steppes northwest of the Black Sea l, the Mikhailovka culture was replaced by the Usatovo culture after 3300 BCE.[46] The Mikhailovka culture at the Crimea developed into the Kemi Oba culture.[46]
- Post-Mariupol culture (early phase 3800-3300 BCE, late phase 3300-2800 BCE):[48] around the Dnieper Rapids, near the Donets River.[49] According to Ina Potekhina, the people looked most like the Suvorovo-Novodanilovka people.[46]
- Late/Phase II Sredny Stog culture (Dniepr-Donets-Don), c. 4000–3500 BCE.[50]
- Repin culture (Don) and late Khvalynsk culture (lower Volga):[51] the Repin culture developedby contact with the late Maikop-Novosvobodyana culture (Lower Don),[52] which penetrated deeply into the Lower Volga steppe.[53] Anthony also believes that Repin was highly significant to the establishment of the Afanasevo culture in eastern Siberia, c. 3700–3300 BCE.[54]
Chapter Thirteen: Wagon Dwellers of the Steppes. The Speakers of Proto-Indo-European
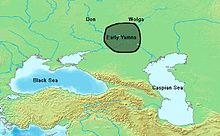
Location of early Yamna culture
The Yamna horizon (3300-2500 BCE)
[55] originated in the Don-Volga area,
[56] where it was preceded
[57] by the Middle Volga's
Khvalynsk culture (4700-3800 BCE)
[18] and the Don-based Repin culture (ca.3950-3300 BCE),
[58] and late pottery from these two cultures can barely be distinguished from early Yamna pottery.
[59] The
Afanasevo culture, at the western Altai Mountains, at the far eastern end of the steppes, was an offshoot from the Repin culture.
[60]
The Yamna horizon was an adaptation to a climate change between 3500 and 3000 BCE. The steppes became drier and cooler, herds needed to be moved frequently to feed them sufficiently, which was made possible by the use of wagons and horseback riding, leading to "a new, more mobile form of pastoralism."
[61] It was accompanied by new social rules and institutions to regulate the local migrations in the steppes, creating a new social awareness of a distinct culture, and of "cultural Others," who did not participate in the new institutions.
[55]
The early Yamnaya horizon spread quickly across the Pontic-Caspian steppes between ca. 3400 and 3200 BCE.
[62] According to Anthony, "the spread of the Yamnaya horizon was the material expression of the spread of late Proto-Indo-European across the Pontic-Caspian steppes."
[63] Anthony further notes that "the Yamnaya horizon is the visible archaeological expression of a social adjustment to high mobility - the invention of the political infrastructure to manage larger herds from mobile homes based in the steppes."
[64]
The Yamna horizon is reflected in the disappearance of long-term settlements between the Don and the Ural and the brief periods of usage of kurgan cemeteries, which begin to appear deep into the steppes between the major river valleys.
[65]
The eastern part (Volga-Ural-North Caucasian) of the Yamna horizon was more mobile than the western part (South Bug-lower Don), which was more farming-oriented.
[66] The eastern part more male-oriented, and the western part was more female-inclusive.
[67] The eastern part also had a higher number of males buried in kurgans, and its deities were male-oriented.
[68]
Chapter Fourteen: The Western Indo-European Languages
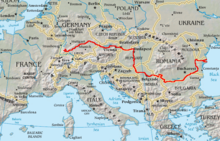
Course of the
Danube, in red
According to Anthony, Pre-Italic, Pre-Celtic and Pre-Germanic may have split off in the
Danube Valley and the Dniestr-Dniepr from Proto-Indo-European.
[69]
The
Usatovo culture developed in southeastern Central Europe at around 3300–3200 BCE at the Dniestr.
[70] Although closely related to the
Tripolye culture, it is contemporary with the Yamna culture and resembles it in significant ways.
[71] According to Anthony, it may have originated with "steppe clans related to the Yamnaya horizon who were able to impose a patron-client relationship on Tripolye farming villages."
[72] According to Anthony, the Pre-Germanic dialects may have developed in the culture between the Dniestr (western Ukraine) and the
Vistula (Poland) in c. 3100–2800 BCE, and spread with the Corded Ware culture.
[73]
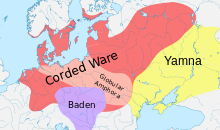
Approximate extent of the Corded Ware horizon with the adjacent 3rd-millennium cultures (
Baden culture and
Globular Amphora culture,
Encyclopedia of Indo-European Culture)
Between 3100–2800/2600 BCE, when the Yamna horizon spread fast across the Pontic Steppe, a real folk migration of Proto-Indo-European-speakers from the Yamna-culture took place into the Danube Valley,
[74] moving along Usatovo territory toward specific destinations, reaching as far as Hungary,
[75] where as many as 3000 kurgans may have been raised.
[76] Bell Beaker sites at Budapest, dated c. 2800–2600 BCE, may have aided in spreading Yamna dialects into Austria and southern Germany in the west, where Proto-Celtic may have developed.
[77] Pre-Italic may have developed in Hungary,l and spread toward Italy via the
Urnfield culture and
Villanovan culture.
[77] According to Anthony, Slavic and Baltic developed in the Middle
Dniepr (Ukraine)
[78] in c. 2800 BCE, spreading north from there.
[79]
The
Corded Ware culture in Middle Europe probably played an essential role in the origin and spread of the
Indo-European languages in Europe during the Copper and Bronze Ages.
[80] According to Anthony, the Corded ware horizon may have introduced Germanic, Baltic and Slavic into Northern Europe.
[77]
Chapter Fifteen: Chariot Warriors of the Northern Steppes
The expansion eastwards of the Corded Ware culture, north of the steppe zone, led to the Sintashta culture, east of the Ural Mountains, which is considered to be the birthplace of the Indo-Iranians.
[81] Anthony skips over the post-Yamna cultures in the steppe zone (Late Yamnaya,
Catacomb (2800-2200 BCE), and
Poltavka (2700-2100 BCE)) but gives an extensive treatment of the intermediate
Middle Dniepr culture (3200-2300 BCE) and of the Corded Ware cultures in the forest zone (
Fatyanova (3200-2300 BCE),
Abashevo (2500-1900 BCE), and
Balanovo (3200-2300 BCE).
[82]
After ca. 2500 BCE, the Eurasian steppes became drier, peaking in ca. 2000 BCE, with the steppes southeast of the Ural mountains becoming even drier than the Middle Volga steppe.
[83] In ca. 2100 BCE, Poltavka and Abashevo herders moved into the upper Tobol and Ural river valleys, close to marshes which were needed for the survival of their herds.
[84] They build fortified stringholds, forming the
Sintashta culture at the southern range of the Ural mountains.
[85] Via the
BMAC, they stood in contact with middle eastern cities like
Ur, and the Sintashta settlements reveal an extensive copper producing industry, producing copper for the Middle Eastern market.
[86] The Sintashta culture was shaped by warfare, which occurred in tandem with a growing long-distance trade.
[87] Chariots were an important weapon in the Sintashta culture and spread from there to the Middle East.
[88]
Anthony notes that "the details of the funeral sacrifices at Sintashta showed startling parallels with the sacrificial funeral rituals of the
Rig Veda."
[81]
Chapter Sixteen: The Opening of the Eurasian Steppes
Steppe cultures between 2200-1800 BCE are the
Multi-cordoned ware culture (2200-1800 BCE)(Dniepr-Don-Volga), Filatovka culture, and
Potapovka. In the forest zone are the Late Middle Dniepr and the Late Abashevo cultures. East of the Urals are the Sintashta and the Petrovka cultures. East of the Caspian Sea is the non-Indo-European Late Kelteminar culture.
[89]
The Catacomb, Poltavka and Potapovka cultures were succeeded by the
Srubna culture, and the Sintashta and Petrovka cultures were succeeded by the
Andronovo culture.
[90]