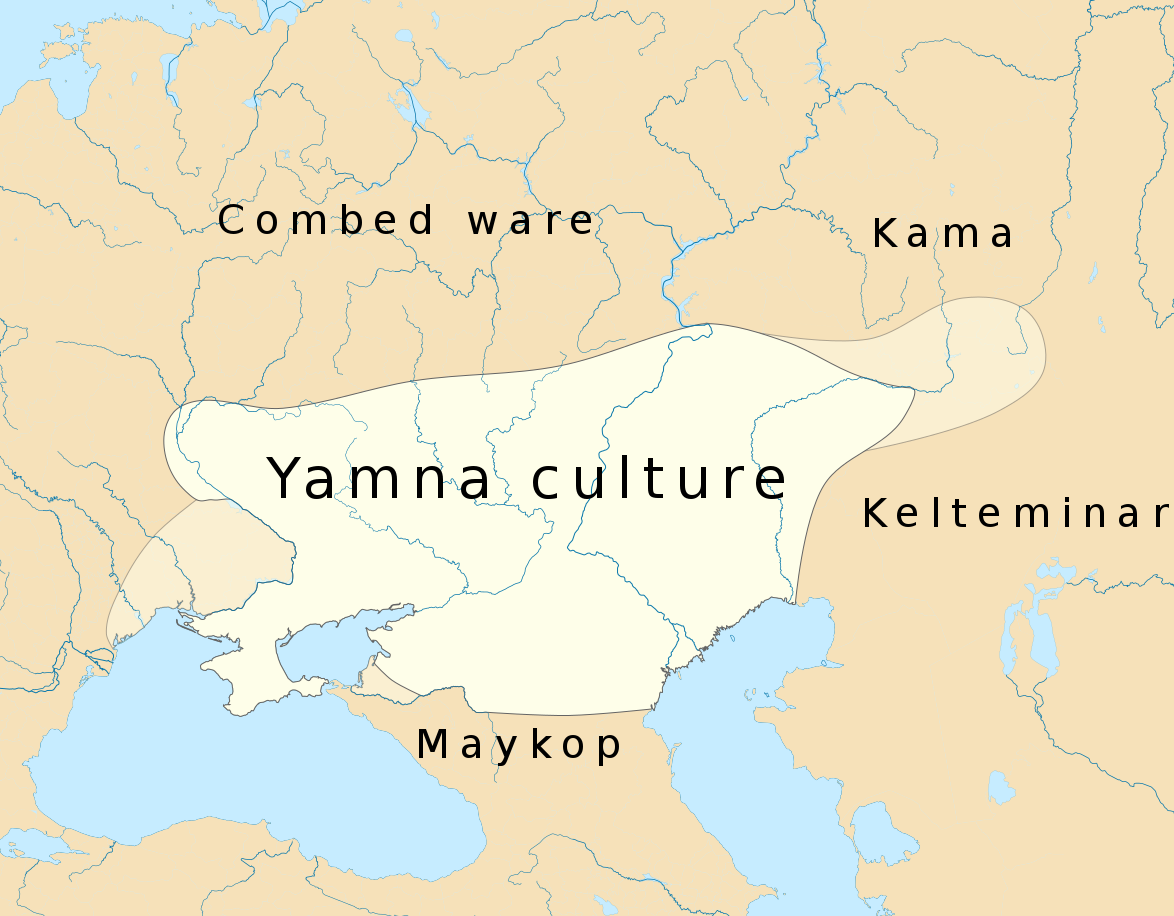
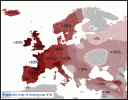
...the data show that the Yamnaya also made a major demographic impact—in fact, it is clear that the single most important source of ancestry across northern Europe today is the Yamnaya or groups closely related to them. This suggests that the Yamnaya expansion likely spread a major new group of languages throughout Europe. The ubiquity of Indo-European languages in Europe over the last few thousand years, and the fact that the Yamnaya-related migration was more recent than the farming one, makes it likely that at least some Indo-European languages in Europe, and perhaps all of them, were spread by the Yamnaya.
His key observation is that all extant branches of the Indo-European language family except for the most anciently diverging Anatolian ones that are now extinct (such as ancient Hittite) have an elaborate shared vocabulary for wagons, including words for axle, harness pole, and wheels. Anthony interpreted this sharing as evidence that all Indo-European languages spoken today, from India in the east to the Atlantic fringe in the west, descend from a language spoken by an ancient population that used wagons. This population could not have lived much earlier than about six thousand years ago, since we know from archaeological evidence that it was around then that wheels and wagons spread. This date rules out the Anatolian farming expansion into Europe between nine thousand and eight thousand years ago. The obvious candidate for dispersing most of today’s Indo-European languages is thus the Yamnaya, who depended on the technology of wagons and wheels that became widespread around five thousand years ago.
This suggests to me that the most likely location of the population that first spoke an Indo-European language was south of the Caucasus Mountains, perhaps in present-day Iran or Armenia, because ancient DNA from people who lived there matches what we would expect for a source population both for the Yamnaya and for ancient Anatolians.
These results reveal a remarkably parallel tale of the prehistories of two similarly sized subcontinents of Eurasia—Europe and India. In both regions, farmers migrating from the core region of the Near East after nine thousand years ago—in Europe from Anatolia, and in India from Iran—brought a transformative new technology, and interbred with the previously established hunter-gatherer populations to form new mixed groups between nine thousand and four thousand years ago. Both subcontinents were then also affected by a second later major migration with an origin in the steppe, in which Yamnaya pastoralists speaking an Indo-European language mixed with the previously established farming population they encountered along the way, in Europe forming the peoples associated with the Corded Ware culture, and in India eventually forming the ANI. These populations of mixed steppe and farmer ancestry then mixed with the previously established farmers of their respective regions, forming the gradients of mixture we see in both subcontinents today.
The period around five thousand years ago north of the Black and Caspian seas corresponds to the rise of the Yamnaya, who, as discussed in part II, took advantage of horses and wheels to exploit the resources of the open steppe for the first time. The genetic data show that the Yamnaya and their descendants were extraordinarily successful, largely displacing the farmers of northern Europe in the west and the hunter-gatherers of central Asia in the east.
Gimbutas argued that the arrival of the Yamnaya in Europe heralded a shift in the power relationships between the sexes. It coincided with the decline of “Old Europe,” which according to Gimbutas was a society with little evidence of violence, and in which females played a central social role as is apparent in the ubiquitous Venus figurines. In her reconstruction, “Old Europe” was replaced by a male-centered society, evident not only in the archaeology but also in the male-centered Greek, Norse, and Hindu mythologies of the Indo-European cultures plausibly spread by the Yamnaya.
...ancient DNA data have provided evidence that the Yamnaya were indeed a society in which power was concentrated among a small number of elite males. The Y chromosomes that the Yamnaya carried were nearly all of a few types, which shows that a limited number of males must have been extraordinarily successful in spreading their genes. In contrast, in their mitochondrial DNA, the Yamnaya had more diverse sequences.
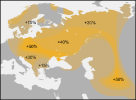
The descendants of the Yamnaya or their close relatives spread their Y chromosomes into Europe and India, and the demographic impact of this expansion was profound, as the Y-chromosome types they carried were absent in Europe and India before the Bronze Age but are predominant in both places today.
...in our data around 90 percent of males who carry Yamnaya ancestry have a Y-chromosome type of steppe origin that was absent in Iberia prior to that time. It is clear that there were extraordinary hierarchies and imbalances in power at work in the expansions from the steppe.