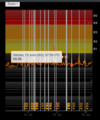
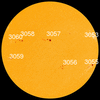
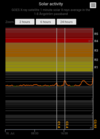
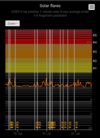
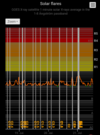
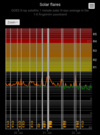
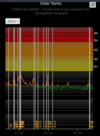
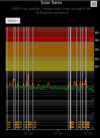
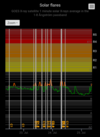
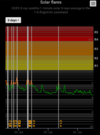
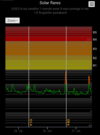
COSMIC RAY UPDATE: Cosmic rays in the atmosphere are rapidly subsiding. In the past year alone, radiation levels in the air high above California have plummeted more than 15%, according to regular launches of cosmic ray balloons by Spaceweather.com and
Earth to Sky Calculus. The latest measurement on July 23, 2022, registered a 6 year low:

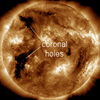
This development, while sudden, is not unexpected. Cosmic rays from deep space are repelled by solar activity; when one goes up, the other goes down. Since 2021, Solar Cycle 25 has
roared to life faster than forecasters expected. The onset of the new solar cycle has naturally led to a decrease in cosmic radiation reaching Earth.
To many readers this may sound counterintuitive. After all, don't solar flares
produce radiation? Yes, but most high-energy radiation doesn't come from the sun; it comes from deep space. Every day
galactic cosmic rays from distant supernova explosions pass through the Solar System. When they hit the top of Earth's atmosphere, they create a secondary spray of radiation, which we measure using sensors onboard our balloons.
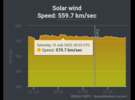
The sun makes it more difficult for these cosmic rays to reach Earth. Simply put, when the sun is active, its magnetic field gets stronger and more tangled. Cosmic rays have trouble penetrating the magnetic thicket. Also, individual CMEs sweep aside cosmic rays, causing sharp reductions called "
Forbush Decreases." The two effects blend together to bring daily radiation levels down.